The Ultimate Guide to Fiber: How Much per Day Do You Need for Optimal Health?

What is Fiber and Why is it Important?
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that your body can’t digest, meaning it passes through your intestinal tract undigested. Unlike other carbohydrates that break down into sugar molecules, fiber remains mostly intact, which is what makes it so beneficial for your digestive system.
Fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy gut. It helps promote regular bowel movements by adding bulk to your stool, which can prevent constipation. Beyond digestion, fiber plays a key role in overall health, supporting heart health, aiding in weight management, and even reducing the risk of certain diseases.
There are two main types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, helping to lower blood cholesterol and glucose levels. Insoluble fiber doesn’t dissolve in water and works by helping material move through your digestive system, which aids in maintaining regular bowel movements.
Understanding the role of fiber in your diet is crucial for making informed dietary choices. Incorporating fiber-rich foods into your meals can significantly contribute to a balanced diet and support optimal health by helping you manage your daily calorie intake.

The Importance of Dietary Fiber
Dietary fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and promoting overall well-being. It works by slowing down digestion, which helps you feel full longer, supporting effective weight management and aiding in the prevention of overeating.
A diet rich in fiber has been shown to lower cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol particles in the digestive system and removing them from the body. Fiber also helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of sugar, which is especially beneficial for people with diabetes. Additionally, it supports healthy blood pressure by promoting better heart health.
Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy gut bacteria, which are vital for digestion and overall immune function. These bacteria ferment certain types of fiber, producing short-chain fatty acids that contribute to gut health and support the immune system. Incorporating high-fiber foods into your diet is a key step towards enhancing your health and preventing chronic diseases.
Calculating Your Recommended Fiber Intake
The recommended daily fiber intake can vary depending on your age, sex, and calorie intake. According to the USDA, it’s generally advised to consume at least 14 grams of fiber for every 1,000 calories you eat. Using a dietary fiber calculator can help you track and optimize your daily fiber intake, promoting weight management, digestion, and nutrient absorption.
To calculate your daily fiber needs, you can use a fiber calculator with the following formula:
• Divide your daily calorie goal by 1,000, and then multiply the result by 14.
For example, if your daily calorie goal is 2,000 calories:
• 2,000 calories ÷ 1,000 = 2
• 2 x 14 grams of fiber = 28 grams of fiber per day
Additionally, a fiber per day calculator offers a user-friendly design to assist individuals in tracking their fiber intake and achieving their dietary goals. This calculation helps ensure that your fiber intake is aligned with your calorie intake, supporting overall health and well-being.

Increasing Your Daily Fiber Intake
To increase your fiber intake and enjoy the associated health benefits, consider incorporating more fiber by adding more whole grains into your diet, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread. These grains are not only high in fiber but also provide essential nutrients that support overall health.
Adding more fruits and vegetables to your meals is another effective way to boost fiber. Aim for a variety of colors to ensure you’re getting a range of nutrients along with your fiber. Fruits like apples, berries, and pears, as well as vegetables like broccoli, carrots, and leafy greens, are all excellent choices.
Don’t forget about legumes, nuts, and seeds. These are not only high in fiber but also add texture and flavor to your meals and snacks. Lentils, chickpeas, chia seeds, and almonds are great options to include in your daily diet for an extra fiber boost.
High Fiber Foods for a Healthy Diet
Adding a variety of high-fiber foods to your diet is essential for promoting digestive health and maintaining overall well-being. Here are some excellent sources of dietary fiber:
• Fruits: Include fiber-rich options like berries (such as strawberries and raspberries), apples, bananas, and citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits. These fruits not only add natural sweetness to your meals but also provide essential vitamins and antioxidants.
• Vegetables: Opt for vegetables like broccoli, carrots, Brussels sprouts, and sweet potatoes. These veggies are packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them essential components of a healthy diet.
• Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and kidney beans are excellent sources of both soluble and insoluble fiber. These foods not only support digestive health but also help maintain regular bowel movements and contribute to overall well-being.They can be added to soups, salads, and stews for a hearty, fiber-filled meal.
• Whole Grains: Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread, and whole grain pasta. These grains retain their natural fiber content and are a healthier alternative to refined grains.
The Role of Fiber in Maintaining a Healthy Gut
Fiber plays a crucial role in promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation by adding bulk to the stool and facilitating its movement through the digestive tract. This helps ensure that waste is efficiently eliminated from the body, reducing the risk of constipation and associated complications.
In addition to its role in digestion, fiber supports the growth of healthy gut bacteria and maintains a balanced gut microbiome. These beneficial bacteria ferment certain types of fiber, producing short-chain fatty acids that nourish the gut lining, reduce inflammation, and enhance overall gut health.
A healthy gut is vital for immune function, as a significant portion of the immune system resides in the gut. By promoting a balanced gut microbiome, fiber contributes to a stronger immune response, better digestion, and overall well-being. Incorporating a variety of fiber-rich foods into your diet is essential for maintaining a healthy gut and supporting your body’s health.
How Fiber Can Help with Weight Loss
Fiber plays a significant role in supporting weight loss by helping you feel fuller for longer, which can naturally reduce calorie intake. Foods high in fiber require more chewing and take longer to eat, giving your body time to signal that it’s full before you overeat. This increased satiety means you’re less likely to reach for extra snacks or overindulge in high-calorie foods, which is crucial for weight management.
Moreover, high-fiber foods are often lower in calories compared to processed, fiber-poor foods. These foods, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, not only provide essential nutrients but also help you maintain a calorie deficit without feeling deprived, which is essential for weight loss.
Aiming for 30 grams of fiber per day can significantly support your weight loss efforts by ensuring that you’re getting enough fiber to stay full, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote a healthy digestive system. Incorporating a variety of fiber-rich foods into your diet can make a big difference in your journey toward a healthier weight.

Fiber Intake and Overall Health: Tips and Common Mistakes
Adequate fiber intake is essential for maintaining overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Fiber plays a crucial role in lowering cholesterol levels, regulating blood sugar levels, and supporting healthy blood pressure. Additionally, it promotes the growth of healthy gut bacteria, which is vital for immune function and overall well-being.
To ensure you’re meeting your daily fiber needs, consider using a fiber intake calculator to determine your individual requirements. Incorporating more whole grains, fruits, and vegetables into your diet is an effective way to boost your fiber intake. However, it’s important to increase your fiber consumption gradually to allow your gut microbiome to adjust, preventing any potential digestive discomfort.
FoodIntake app food tracker will help you monitor amount of micronutrients in your meals and foods including fiber:
Be mindful of common mistakes when increasing your fiber intake. Consuming too much fiber too quickly can lead to digestive issues like bloating and discomfort. Additionally, not drinking enough water can exacerbate these effects, as fiber needs water to move smoothly through the digestive system. It’s also important to focus on getting fiber from whole foods rather than relying on supplements, as whole foods provide additional nutrients that support overall health.
By understanding the importance of fiber and implementing these tips, you can effectively support your health while avoiding common pitfalls.
How can I get 25 grams of fiber a day?
Include foods like beans, lentils, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and nuts. For example, a combination of a cup of lentils, an apple, a serving of broccoli, and a handful of almonds can help you reach 25 grams.
What food is the highest in fiber?
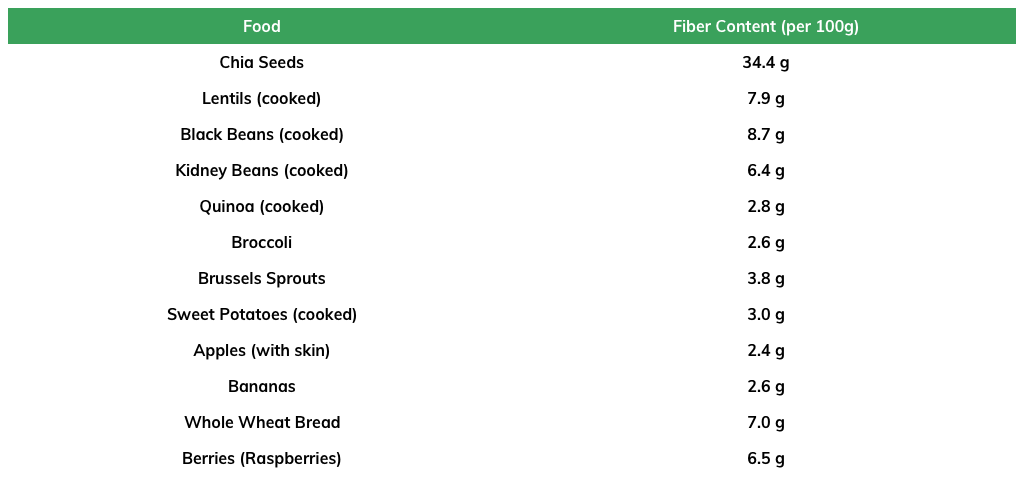
Chia seeds are among the highest, with about 34.4 grams of fiber per 100 grams.
How much fiber should I eat a day to poop regularly?
Aim for at least 25-30 grams of fiber daily to support regular bowel movements.
How much fiber per day to lose weight?
Consuming around 30 grams of fiber per day can help you feel fuller longer and support weight loss.
How do I calculate my fiber intake?
Track your food intake using a nutrition app or food diary to answer the question 'how much fiber do I need' by listing the fiber content of each food item.
How do you calculate fiber percentage in food?
Divide the grams of fiber by the total grams of the food item, then multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
What do 25 grams of fiber look like in a day?
This might include a bowl of oatmeal (4g), an apple (4g), a cup of lentils (15g), and a serving of broccoli (5g).
How to get 25 to 30 grams of fiber a day?
Incorporate a variety of high-fiber foods like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts throughout your meals.
How to calculate DRI for fiber?
The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) for fiber is generally calculated based on 14 grams of fiber per 1,000 calories consumed.
How to measure dietary fiber intake?
Use a food tracking app or check nutrition labels to sum up the grams of fiber in your daily diet.
Does fiber help you lose belly fat?
While fiber alone doesn’t specifically target belly fat, it can help with overall weight loss by increasing satiety and reducing calorie intake.
What is the best fiber for weight loss?
Soluble fiber, found in oats, barley, and beans, is particularly effective in promoting fullness and reducing calorie intake.
How is fiber calculated?
Fiber content is typically measured in grams per serving and listed on nutrition labels.
How do you calculate the fiber ratio?
The fiber ratio can be calculated by dividing the fiber content by the total carbohydrate content and multiplying by 100.
How much fiber should a 200-pound man eat?
A general recommendation is 25-30 grams per day, but individual needs can vary based on calorie intake and activity level.
Is 50g of fiber too much?
For most people, 50 grams might be excessive and could lead to digestive discomfort. It’s important to increase fiber gradually and drink plenty of water.
How many grams of fiber should I eat on a 1500 calorie diet?
Aim for around 21 grams of fiber (based on the guideline of 14 grams per 1,000 calories).
What foods are highest in fiber?
High-fiber foods include legumes (lentils, beans), whole grains (quinoa, oats), fruits (raspberries, pears), and vegetables (broccoli, Brussels sprouts).






