How to Calculate Your Daily Sugar Intake: A Free Sugar Intake Calculator Guide

Understanding Sugar Intake
What is Sugar Intake?
Sugar intake refers to the amount of sugar you consume daily through various food and beverages. Understanding and managing your sugar intake is vital for maintaining a balanced diet and preventing health issues like diabetes and heart disease. The American Heart Association advises limiting daily sugar intake to no more than 6 teaspoons for women and 9 teaspoons for men, yet many people unknowingly exceed these limits due to hidden sugars in processed foods. Additionally, fruit juices, often perceived as a healthy option, can contain high sugar content similar to sugary beverages, raising awareness about the potential pitfalls of consuming them without considering their sugar levels.
Monitoring sugar intake is crucial as excessive sugar consumption is linked to rapid weight gain, obesity, and chronic diseases. Added sugars, particularly from processed foods and sugary drinks, contribute empty calories that can disrupt a balanced diet and lead to nutritional deficiencies. High fructose corn syrup, a common added sugar, is especially problematic as it can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, contributing to metabolic issues.
To effectively manage sugar consumption, it’s important to be aware of hidden sugars and use tools like a sugar intake calculator. These tools can help you track your daily sugar intake and ensure you stay within recommended limits, reducing the risk of health problems associated with high sugar consumption.
Recommended Daily Sugar Limits
How Much Sugar is Too Much?
- Consuming more than the recommended daily sugar limit can lead to health issues like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
- The daily sugar limit varies depending on age, gender, and activity level.
- The FDA proposes a daily added sugar intake of 10% of daily calories, which is about 50 grams (12 teaspoons) per day for a 2000-calorie diet.
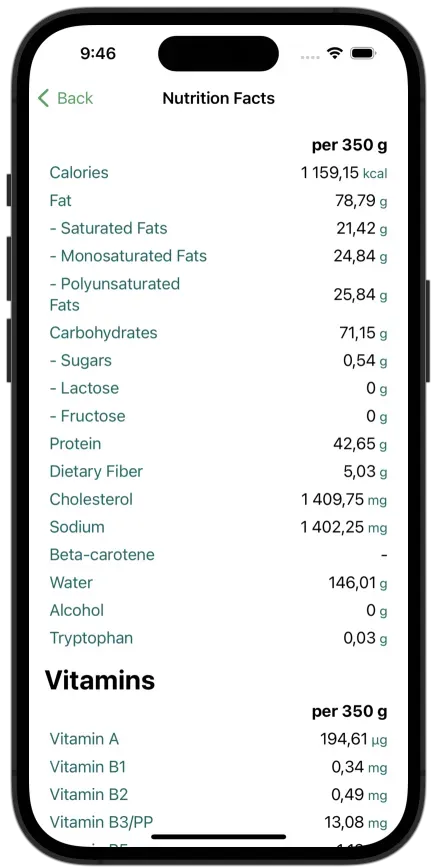
FoodIntake app AI calorie counting app is a great companion to help you effortlessly track your sugar intake, macros and calories:
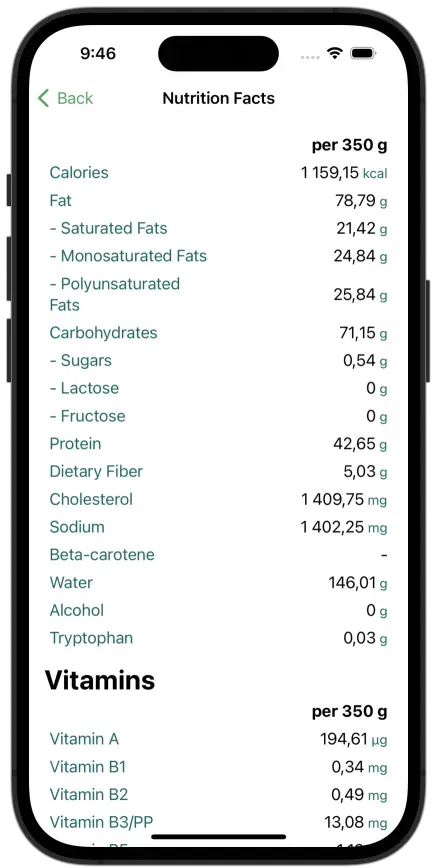
Calculating Daily Sugar Intake
Using a Sugar Intake Calculator
Exceeding the recommended daily sugar limit can significantly increase the risk of health problems such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
The appropriate daily sugar limit depends on factors like age, gender, and activity level.
The FDA suggests that added sugars should make up no more than 10% of your daily calorie intake, which equates to about 50 grams or 12 teaspoons per day for someone following a 2,000-calorie diet.

High-In-Sugar Foods and Drinks
Sugary Beverages and Foods
Sugary beverages like soda, sports drinks, and fruit juice concentrates can contain high amounts of added sugars.
1. Soda (Cola) - 39 grams of sugar per 12-ounce (1.5 cups) can
2. Fruit Juice Concentrate - 45 grams of sugar per 1 cup
3. Sports Drinks - 34 grams of sugar per 1 cup
4. Chocolate Milk - 24 grams of sugar per 1 cup
5. Sweetened Yogurt - 47 grams of sugar per 1 cup
6. Ice Cream - 28 grams of sugar per 1 cup
7. Candy (Gummies) - 38 grams of sugar per 1 cup
8. Granola Bars - 25 grams of sugar per 1 cup
9. Packaged Cookies - 44 grams of sugar per 1 cup
10. Breakfast Cereals - 37 grams of sugar per 1 cup
Foods like baked goods, candy, and processed snacks are also high in added sugars.
1. Packaged Cookies - 16 grams of sugar per 2 cookies (approximately 30 grams)
2. Cupcakes - 24 grams of sugar per cupcake (approximately 80 grams)
3. Donuts - 15 grams of sugar per donut (approximately 50 grams)
4. Candy (Milk Chocolate Bar) - 23 grams of sugar per 1 bar (approximately 42 grams)
5. Brownies - 20 grams of sugar per 1 brownie (approximately 60 grams)
6. Fruit Snacks - 19 grams of sugar per small pack (approximately 28 grams)
7. Cinnamon Rolls - 22 grams of sugar per roll (approximately 100 grams)
8. Frosted Breakfast Pastries - 16 grams of sugar per 1 pastry (approximately 52 grams)
9. Granola Bars - 12 grams of sugar per 1 bar (approximately 40 grams)
10. Sweetened Muffins - 21 grams of sugar per muffin (approximately 100 grams)
Consuming high-in-sugar foods and drinks can lead to excessive sugar intake.

Hidden Sources of Added Sugars
Condiments, Sauces, and Packaged Snacks
Condiments such as ketchup and sauces often contain hidden sources of added sugars, making it easy to exceed your daily sugar limit without realizing it.
Similarly, packaged snacks like granola bars and energy bars can be surprisingly high in added sugars, despite their seemingly healthy image.
To avoid excessive sugar intake, it’s crucial to read nutrition labels carefully, allowing you to identify and manage hidden sources of added sugars in your diet.
Reducing Daily Sugar Intake
Cutting Down on Sugars
Reducing your daily sugar intake can be effectively achieved by cutting down on sugary beverages and foods that contribute to excessive sugar consumption.
Opting for products with natural sugars, such as whole fruits, instead of those with added sugars, can also support healthier eating habits.
Gradually decreasing your sugar intake allows your body to adjust more easily, helping you transition to a healthier diet without feeling deprived.
Artificial Sweeteners vs Sugar
Pros and Cons of Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame and sucralose, offer a sugar-free alternative that can help reduce overall sugar intake, potentially aiding in weight management and lowering the risk of diabetes.
However, excessive consumption of artificial sweeteners may lead to side effects like digestive issues or altered taste perception, and some studies suggest potential long-term health concerns.
Understanding the pros and cons of artificial sweeteners is crucial for making informed dietary choices, balancing the benefits of reduced sugar intake with potential risks associated with artificial alternatives.

Dorito theory and Dorito effect
The Dorito Theory is an idea that explores how food companies enhance the flavor and appeal of processed foods to make them more addictive. The theory suggests that by carefully crafting the taste, texture, and even the sound of certain foods (like the crunch of a Dorito chip), manufacturers can create products that are almost irresistible to consumers. These foods are engineered to deliver a powerful sensory experience that encourages overeating, often leading to unhealthy dietary habits.
What is the Dorito Effect?
The Dorito Effect refers to the phenomenon where processed foods are made to taste far more flavorful than their natural counterparts, leading to an imbalance in our diet. This effect is named after Doritos, a brand of flavored tortilla chips, which are designed to be intensely flavourful and stimulating. The Dorito Effect highlights how artificial flavorings and additives in modern processed foods can trick our brains into craving these foods more than whole, unprocessed foods, potentially leading to overconsumption and negative health outcomes.

Added Sugar Intake and Health
The Impact of Added Sugars on Health
Excessive consumption of added sugars is strongly linked to significant health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
In addition to these well-known risks, added sugars may also increase the likelihood of developing certain cancers and contribute to cognitive decline over time.
For optimal health, it is crucial to reduce added sugar intake, focusing on a diet rich in whole foods and low in processed, sugar-laden products.
Making Informed Choices
Reading Labels and Making Healthy Choices
Reading food labels is a crucial step in identifying hidden added sugars in your diet, helping you make more informed choices.
Opting for products with natural sugars, such as those found in whole fruits, instead of those with added sugars, can significantly reduce your overall sugar intake.
By making these informed choices, you can maintain a healthier diet and lower your risk of chronic diseases like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
Takeaways
Importance of Monitoring Daily Sugar Intake
Monitoring your daily sugar intake is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet and lowering the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, obesity, and heart disease.
By understanding how to calculate your daily sugar intake and identifying hidden sources of added sugars, you can make more informed dietary choices that support your health goals.
Reducing your daily sugar intake can lead to numerous health benefits, including improved overall well-being, better weight management, and a decreased likelihood of developing chronic health conditions.