Muscle gain protein calculator. How much protein in foods?

Understanding Protein. What is Protein?
Proteins are one of three primary macro nutrients providing energy to the human body, along with fats and carbohydrates. They are responsible for cell structure and function, and regulate various bodily processes. Proteins are composed of amino acids, with 20 different types in total. Amino acids are necessary for proper body function and can only be obtained through dietary sources as the body cannot produce them on its own.
Essential Amino Acids
The Building Blocks of Protein
What are Amino Acids?
Amino acids are organic compounds that combine to form proteins, which are critical for the body’s structure, function, and regulation of tissues and organs. There are 20 different amino acids, and nine of them are considered essential. Amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through dietary sources.
The Nine Essential Amino Acids
1. Histidine: Important for growth and tissue repair, and the production of histamine, which is vital for the immune response.
2. Isoleucine: A branched-chain amino acid that aids in muscle metabolism and is heavily concentrated in muscle tissue.
3. Leucine: Another branched-chain amino acid crucial for protein synthesis and muscle repair.
4. Lysine: Plays a significant role in protein synthesis, hormone and enzyme production, and calcium absorption.
5. Methionine: Important for metabolism and detoxification, as well as for absorbing zinc and selenium.
6. Phenylalanine: Precursor for neurotransmitters like tyrosine, dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine.
7. Threonine: Integral in the formation of collagen and elastin, and plays a role in fat metabolism.
8. Tryptophan: Precursor for serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, sleep, and appetite.
9. Valine: Another branched-chain amino acid essential for muscle growth and energy production.
Sources of Amino Acids
These amino acids can be found in both animal and plant-based foods. Here are some examples of rich sources:
• Animal Sources: Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
• Plant Sources: Quinoa, buckwheat, soy, chia seeds, and legumes.
Importance of Essential Amino Acids
Essential amino acids are crucial for various bodily functions, including:
• Protein Synthesis: They are the building blocks for protein creation, necessary for muscle growth and repair.
• Enzyme and Hormone Production: Essential for the synthesis of enzymes and hormones that regulate bodily processes.
• Immune Function: Support the immune system by producing antibodies.
• Energy Production: Some amino acids are metabolized to provide energy.
Combining Incomplete Proteins
Plant-based foods often lack one or more essential amino acids, making them incomplete proteins. However, combining different plant-based proteins can provide all essential amino acids. For example, rice and beans together offer a complete protein profile.

Determining Your Protein Needs
Age: older adults may require more protein to prevent muscle loss. Sex: pregnant and lactating women require more protein for fetal development and milk production. Activity level: athletes and bodybuilders require more protein for muscle mass and repair. Health conditions: individuals with kidney disease or liver disease may require different protein intake recommendations. Vegetarians and vegans may require more protein from plant-based sources.
Calorie per gram of protein
Calories come from three primary macronutrients: proteins, carbs, and fats. Proteins provide 4 calories per gram, produce enzymes and hormones, and support growth and development. They serve as the building blocks for the body’s structural and functional components. While proteins can provide energy, their primary role is more structural. Carbs, also providing 4 calories per gram, are the body’s preferred energy source, particularly for brain function and high-intensity activities. They are broken down into glucose, which is either used immediately for energy or stored as glycogen. Fats, offering 9 calories per gram, are the most energy-dense macronutrient and play crucial roles in supporting cell growth, protecting organs, and aiding the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. For those focusing on building more muscle, a higher protein intake is beneficial, especially when paired with intense exercise. A balanced diet should include an appropriate proportion of calories from all three macronutrients to ensure optimal health, tailored to individual goals and activity levels.
Best protein tracker
If you tired of writing down your protein intakes and want to log it on autopilot consider FoodIntake app effortless protein, carbs, fats tracker, logger. Powered by AI and official data from such providers as USDA/FDA, CNF, and others:
How Much Protein Do You Need?
Protein requirements depend on energy intake, growth, and physical activity level. Recommended dietary allowance (RDA) is 0.8g/kg or 0.36g per pound of body weight, but individual needs may vary. This value is the minimum recommended value to maintain basic nutritional requirements. Consuming more protein, up to a certain point, may be beneficial for more muscle and overall health.
The Best Protein food Calculator: Find Your Ideal Daily Protein Intake
A protein calculator is a tool designed to estimate optimal protein intake based on age, weight, height, gender, activity level, and fitness goals. Protein calculators can help determine individual protein needs and provide a personalised recommendation. Using a protein calculator can help ensure you are meeting your daily protein needs and support muscle growth and overall health.
Protein calculator
Our free calculator allows you to see your total daily energy expenditure calories and macro nutrients distribution ranges along with your required minimum protein intake.
Choosing High-Quality Protein Sources
Complete protein sources contain all amino acids, including meat, dairy, eggs, and fish. Incomplete proteins, like legumes, grains, and nuts, can be combined to meet protein needs. High-quality protein sources are rich in amino acids and have a high bioavailability. High-quality protein sources include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based options such as beans and lentils and other legumes.
Meeting Your Daily Protein Needs
RDA suggests to consume 0.8-1.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. Space out protein intake throughout the day to support building of more muscle and their repair. Choose a variety of high-quality protein sources to meet daily protein needs. Consider using a protein supplement if you are struggling to meet your daily protein needs through whole foods.

Foods highest in protein
Meals highest in protein
1. Grilled Chicken Breast: 27.5g of protein per 100g
2. Lean Beef Steak: 34.4g of protein per 100g
3. Salmon Fillet: 23g of protein per 100g
4. Turkey Breast: 31g of protein per 100g
5. Tofu Stir-Fry: 17.2g of protein per 100g
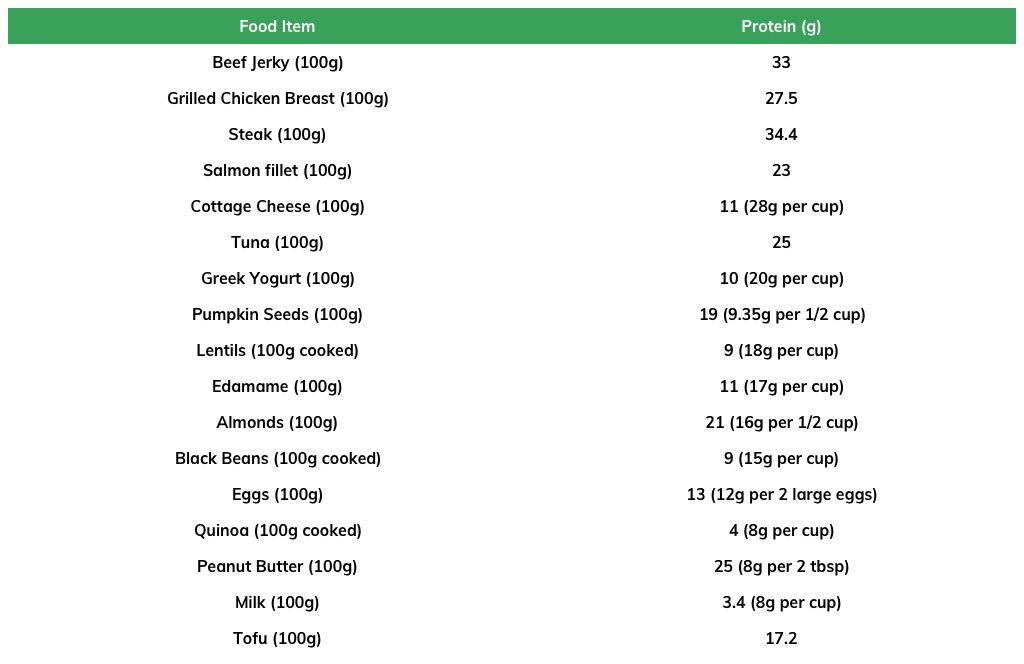
Snacks highest in protein
1. Greek Yogurt: 11g of protein per 100g
2. Hard-Boiled Eggs: 6g of protein per egg
3. Almonds: 6g of protein per 30g
4. Cottage Cheese: 11g of protein per 100g
5. Protein Bars: 20g of protein per bar

Protein supplements
Protein supplements come in various forms, including powders, bars, and ready-to-drink shakes. They are a convenient way to increase protein intake, especially for those who find it challenging to get enough protein from whole foods alone. Common types of protein supplements include whey, casein, soy, pea, rice, and hemp protein.
Pros of Protein Supplements
• Convenient and easy to use
• Can help meet daily protein needs
• Supports muscle growth and recovery
Cons of Protein Supplements
• Potential digestive issues
• Can be expensive
• Possible additives and artificial ingredients
Types of Protein Supplements
1. Whey Protein: Derived from milk, it is a complete protein with all amino acids and is known for its quick digestion and absorption.
2. Casein Protein: Also derived from milk, it digests slower than whey, providing a steady release of amino acids.
3. Soy Protein: Plant-based and complete protein, suitable for vegetarians and vegans.
4. Pea Protein: Hypoallergenic and easily digestible, suitable for those with allergies to dairy or soy.
5. Rice Protein: Incomplete protein but often combined with pea protein to provide a complete amino acid profile.
6. Hemp Protein: Plant-based and contains omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, but is not a complete protein.

Supplements and Digestive Health
Supplements are often made by extracting proteins from their natural sources and processing them into powders. For example, whey protein is a byproduct of cheese production, while plant-based proteins are typically extracted from peas, soy, or rice. While supplements can be a convenient and healthy way to boost protein intake, they can sometimes cause digestive issues such as bloating or gas, especially for those with lactose intolerance or sensitivities to certain ingredients.
Some individuals may experience digestive issues when consuming protein supplements, such as bloating, gas, or constipation. These issues can arise from:
• Artificial Additives: Sweeteners, flavorings, and preservatives can cause digestive discomfort.
• High Fiber Content: Some plant-based proteins have high fiber content, excess of which may cause gas and bloating.
• Protein Overload: Consuming large amounts of protein in one sitting can overwhelm the digestive system.
Tips to Avoid Digestive Issues
1. Choose High-Quality Supplements: Look for products with minimal additives and fillers.
2. Start Slowly: Gradually increase protein supplement intake to allow your body to adjust to extra protein.
3. Hydrate: Drink plenty of water to aid digestion.
4. Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you experience persistent issues, consult a healthcare provider for personalised advice.

Common Allergens in Protein Supplements
• Whey and Casein: Derived from milk, these can cause allergic reactions in individuals with dairy allergies. Symptoms may include hives, swelling, respiratory issues, and gastrointestinal distress.
• Soy: Soy allergies can cause reactions such as itching, swelling, and anaphylaxis in severe cases.
• Egg Protein: Made from egg whites, this can trigger allergic reactions in those with egg allergies.
Hypoallergenic Options
For those with allergies, hypoallergenic protein supplements are available, such as:
• Pea Protein: Free from dairy, soy, and gluten, making it a suitable option for most food allergies.
• Rice Protein: Typically hypoallergenic and easy to digest.
• Hemp Protein: Another hypoallergenic option that is also plant-based.
Issues for Lactose-Intolerant Individuals
Lactose intolerance occurs when the body lacks lactase, an enzyme needed to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk. Symptoms include bloating, gas, diarrhea, and stomach cramps after consuming dairy products.
Lactose-Free Protein Supplements
• Whey Isolate: This form of protein has most of the lactose removed and may be tolerable for some lactose-intolerant individuals.
• Plant-Based Proteins: Soy, pea, rice, and hemp proteins are all lactose-free and suitable for those with lactose intolerance.
• Egg White Protein: Free from lactose and a complete protein source.
Putting it All Together
Protein is an essential nutrient for overall health and muscle growth. Determining individual protein needs is important for optimal health and fitness. Using a protein calculator and choosing high-quality protein sources can help ensure you are meeting your daily protein needs. Aim to consume enough protein to support muscle growth and overall health, and consider consulting with a healthcare professional, doctor or registered dietitian for personalised recommendations.






